Understanding the Basics of Gardening
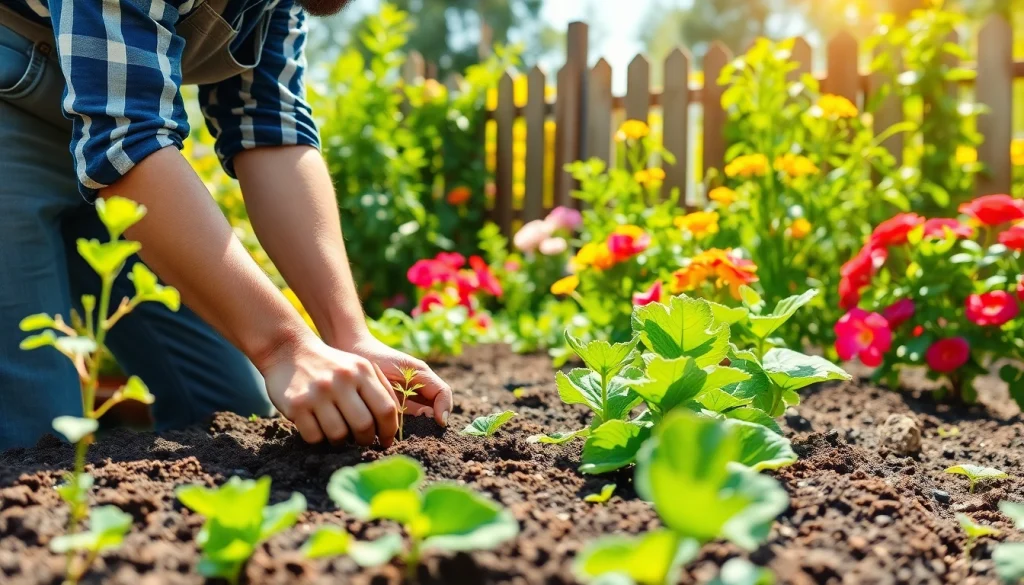
Gardening is more than just a hobby; it is an art and a science that can transform spaces into lush paradises filled with vibrant colors and scents. Engaging in Gardening allows individuals to nurture the environment, cultivate vegetables, herbs, and flowers, and promote overall well-being. From the joy of planting seeds to the satisfaction of harvesting produce, the experience can significantly enhance one’s quality of life. For those looking to embark on this rewarding journey, understanding the fundamentals is essential. This comprehensive guide dives into the core aspects of Gardening to help aspiring green thumbs cultivate their passion effectively. If you’re ready to explore the world of Gardening, you can find valuable resources on Gardening.
What is Gardening?
Gardening refers to the act of cultivating and nurturing plants, whether for aesthetic purposes, food production, or environmental enhancements. It encompasses a variety of practices, ranging from raising ornamental flowers and shrubs to growing edible plants. The essence of Gardening lies in understanding the relationship between plants and their environment, along with managing how these elements interact over time.
Essential Gardening Tools for Beginners
Starting your Gardening journey requires the right tools to ensure efficiency and effectiveness. Here are some essential tools every beginner should have:
- Hand Trowel: Perfect for planting and transplanting small plants.
- Pruning Shears: Ideal for cutting back plants and harvesting crops.
- Garden Fork: Useful for loosening and turning soil.
- Rake: Helps in clearing debris and leveling soil.
- Watering Can: Essential for providing moisture to younger plants and seedlings.
- Gloves: Protect your hands from dirt, thorns, and pests.
The Importance of Soil Quality in Gardening
Soil is often termed as the ‘heart’ of any garden, and for good reason. The quality of soil directly influences plant health and productivity. Healthy soil is teeming with microorganisms and organic matter, which helps retain moisture and provides essential nutrients.
Before planting, assess your soil’s texture, composition, and pH level. Consider adding amendments such as compost, peat moss, or minerals to enrich the soil. Regularly testing your soil can help maintain its health over time.
Planning Your Gardening Space
Choosing the Right Location for Gardening
Location plays a crucial role in successful Gardening. Here are key factors to consider when choosing a site:
- Sunlight: Most vegetables and flowers require at least six hours of sunlight daily.
- Drainage: Ensure the area drains well; standing water can harm roots.
- Accessibility: Choose a spot that is easy to reach for regular maintenance.
- Proximity to Water: Consider how you will water your plants; a nearby source can save time.
How to Design Your Garden Layout
Once you’ve selected a site, it’s time to design your garden layout. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Begin with a sketch of the area to visualize plant placement.
- Group plants with similar water and sunlight needs together.
- Use raised beds to improve drainage and soil quality.
- Incorporate pathways to access various parts of the garden without compacting the soil.
Companion Planting Techniques in Gardening
Companion planting involves pairing plants that benefit each other. Some classic pairings include:
- Tomatoes and Basil: Basil can improve growth and flavor of tomatoes while repelling pests.
- Corn and Beans: Corn provides support for beans while beans enrich the soil with nitrogen.
- Carrots and Onions: Onions can repel carrot flies, protecting the carrots.
Planting and Care Techniques
Best Practices for Planting Seeds
Successful seed planting starts with choosing quality seeds suited to your climate and soil conditions. Here are some best practices:
- Check the seed package for information on planting depth and spacing.
- Plant during the recommended season for best results.
- Consider starting seeds indoors if your growing season is short.
- Water the seeds gently to avoid displacing them.
Watering Schedules for Healthy Gardening
Watering is critical for plant health but must be done correctly to avoid over- or under-watering. Here are tips for establishing a watering schedule:
- Water deeply rather than frequently, aiming for about 1 inch of water per week.
- Utilize a soaker hose or drip irrigation to keep foliage dry and reduce disease risk.
- Water early in the morning to prevent evaporation.
Pest Management Strategies in Gardening
Pest management is essential to protect plants from various threats. Consider these strategies:
- Integrate beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings that feed on pests.
- Implement physical barriers such as nets or row covers.
- Utilize organic pesticides as a last resort, ensuring they are safe for the environment.
Gardening for Sustainability
Exploring Organic Gardening Methods
Organic gardening emphasizes nurturing the ecosystem and avoiding synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. Here are tips for starting an organic garden:
- Use natural fertilizers such as compost or manure.
- Practice crop rotation to maintain soil health.
- Avoid GMOs and choose heirloom varieties for biodiversity.
How to Create a Composting System
Composting is a sustainable way to recycle organic waste and improve soil health. Here’s how to establish your composting system:
- Select a compost bin or designate a compost pile area.
- Add a mix of greens (nitrogen-rich materials like fruit scraps) and browns (carbon-rich materials like dried leaves).
- Maintain moisture but avoid saturation; turn the pile regularly to encourage aeration and decomposition.
- After a few months, harvest your finished compost to enrich your garden soil.
Benefits of Native Plants in Gardening
Incorporating native plants into your garden can yield numerous benefits:
- Native plants require less water and are more drought-resistant.
- They support local wildlife, including pollinators like bees and butterflies.
- Native plants are often more disease-resistant and require fewer chemicals.
Advanced Gardening Strategies
Seasonal Gardening and Plant Rotation
Understanding the seasons is vital in Gardening. Seasonal gardening allows for continuous harvests and nutrient conservation:
- Employ crop rotation, switching out different plant families each season.
- Utilize cover crops in the offseason to improve soil health.
- Adapt planting based on seasonal changes to maximize yield and plant health.
Using Technology to Enhance Gardening Practices
Technology can significantly enhance gardening practices through tools and applications designed to improve efficiency:
- Garden planning apps can assist with layout and scheduling.
- Soil moisture sensors can monitor the moisture levels and prevent overwatering.
- Online forums and resources can help with troubleshooting plant issues and provide community support.
The Artistic Aspect of Gardening Design
Gardening is an adventure of creativity and design. Here are some considerations to integrate artistic elements into your garden:
- Choose a theme for your garden (e.g., Japanese Zen, rustic, modern).
- Incorporate decorative elements such as sculptures, paths, and seating areas.
- Utilize color palettes by mixing flowering plants to create visually appealing spaces.