Introduction to Sports Broadcasting
In today’s world, Sports Broadcasting plays a critical role in how fans engage with their favorite sports, teams, and athletes. The fusion of technology and entertainment has transformed the way sports are delivered to audiences, making it an essential aspect not just for fans but for the entire sports industry. This article delves deep into the realm of sports broadcasting, exploring its evolution, technicalities, and the strategic measures taken to engage audiences effectively.
Understanding the Basics of Sports Broadcasting
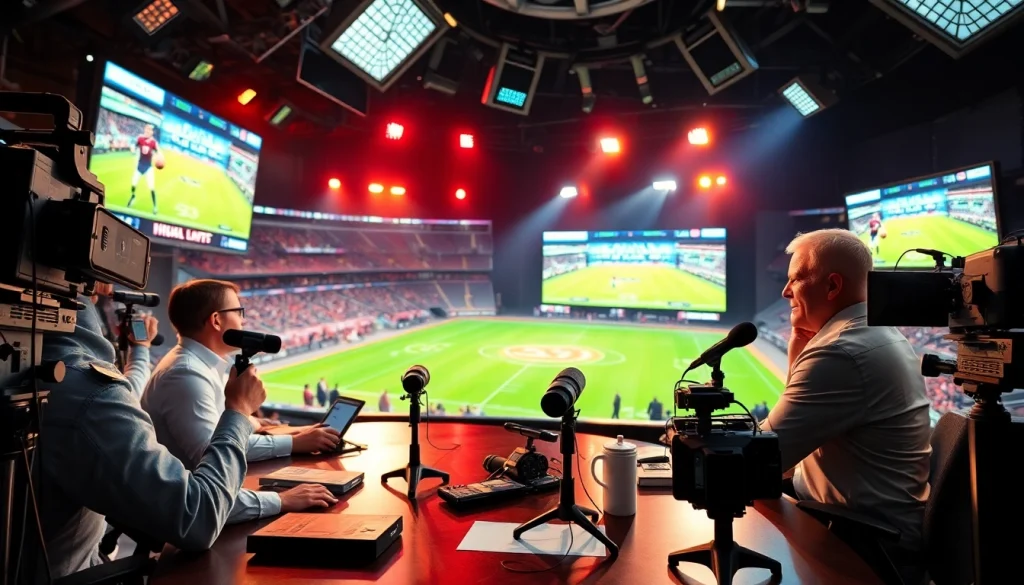
Sports broadcasting encompasses live coverage, analysis, and commentary of sporting events through multiple platforms such as television, radio, and online streaming services. The sector serves a dual purpose: reporting the events and creating an immersive experience for viewers. A well-crafted broadcast can transform a simple sports match into a compelling narrative that captivates audiences.
The basic elements include the commentators—who provide play-by-play and color commentary—the production team responsible for technical operations, and the analysts who break down performances and strategies.
The Evolution of Sports Broadcasting
The journey of sports broadcasting began in the early 20th century with radio transmissions. Over the decades, the landscape has dramatically changed due to technological advancements. The onset of television transformed viewers’ experience, making it more vivid and engaging. In the late 20th century, the internet introduced live streaming, providing fans with unprecedented access to games regardless of their geographical location.
Today, sports broadcasting continues to evolve with innovations such as 4K streaming, viewer interactivity via second screens, and integration with social media platforms, constantly reshaping how audiences consume content.
Key Roles in Sports Broadcasting
The success of sports broadcasting relies on a wide array of professionals. Each role serves a unique purpose, facilitating a seamless viewing experience. Notable positions include:
- Commentators: They narrate the action in real-time, providing context and excitement.
- Producers: They oversee the broadcast’s overall production, including the coordination of various teams.
- Technical Crew: This team manages the cameras, sound equipment, and lighting.
- Analysts: They offer strategic insights and player statistics to enhance viewer understanding.
- Graphic Designers: They create visuals—such as scoreboards and player stats—that enrich the storytelling.
Technical Aspects of Sports Broadcasting
Understanding the technical components of sports broadcasting is crucial for delivering high-quality content. The right equipment and software not only enhance the viewer experience but also streamline production processes, providing reliable outputs.
Essential Equipment for Live Coverage
Quality sports broadcasting hinges on several key pieces of equipment. Fundamental tools include:
- Cameras: High-definition cameras capture live action and are critical for audience engagement.
- Microphones: Quality audio capture is essential for in-depth commentary and fan experiences.
- Mixing Consoles: These devices manage audio inputs from commentators, live feedback, and crowd sounds.
- Switchers: Used to alternate between different camera feeds and graphic displays.
Investing in reliable equipment significantly contributes to the quality of each broadcast, enhancing how content is delivered to the audience.
Broadcasting Software and Streaming Platforms
The rise of digital media has given birth to advanced broadcasting software and streaming platforms that allow for smooth live coverage. Some essential tools include:
- Streamlining Software: Programs such as Wirecast and OBS Studio facilitate live streaming and provide graphic overlays.
- Analytics Tools: These offer insights into viewer engagement and demographics, helping sports organizations tailor their content.
- Content Management Systems: These systems organize and distribute broadcast content across various platforms, ensuring consistency.
With digital broadcasting gaining traction, investing in the right software is vital for effective communication and engagement.
Effective Use of Graphics and Analytics
Visual elements coupled with data analytics significantly enhance storytelling in sports broadcasting. Graphics—which include real-time stats, player information, and game insights—can contextualize the action on-screen. Moreover, analytics help broadcasters tailor their offerings based on viewer preferences and behaviors, ensuring that content is engaging and relevant.
By incorporating comprehensive graphics and analytics, broadcasters can create an enriching experience that combines entertainment and information for their audiences.
Audience Engagement Techniques in Sports Broadcasting
Sports broadcasting is not just about delivering content—it’s about creating a community. Implementing effective engagement strategies can foster a strong connection between the broadcasters and their audience.
Building a Loyal Fanbase
Building a loyal fanbase requires consistent, engaging content and a genuine understanding of audience interests. Strategies include:
- Interactive Content: Polls, quizzes, or live Q&A sessions can actively involve viewers.
- Community Initiatives: Hosting viewer parties or events promotes a sense of belonging.
- Regular Feedback: Listening to audience feedback can help tailor programming to meet viewer needs.
Developing long-term relationships with viewers results in a dedicated fan base that supports the broadcast.
Utilizing Social Media for Interaction
Social media platforms act as an extension of sports broadcasts, providing real-time interaction and engagement. By leveraging platforms such as Twitter, Instagram, and Facebook, broadcasters can:
- Share Highlights: Instant replays and standout moments can be shared in real time.
- Engage with Fans: Respond to comments, host live chats, and share behind-the-scenes content.
- Promote Events: Using social media as promotional tools for upcoming matches or content helps attract viewers.
Harnessing the power of social media not only boosts engagement but also broadens the audience base.
Incorporating Viewer Feedback
Both qualitative and quantitative feedback from viewers is invaluable in shaping future broadcasts. Collecting audience insights via surveys, social media engagement, or comment sections can guide decision-making processes. Examples include adjusting game timings, enhancing commentary style, or introducing popular segments based on viewer preferences. This iterative process builds viewer loyalty and ensures continued audience growth.
Challenges Faced in Sports Broadcasting
While sports broadcasting presents myriad opportunities, several challenges can arise that need to be effectively managed for successful outcomes.
Handling Breaking News and Injury Reports
In the fast-paced environment of sports, breaking news—like trades or injuries—demands rapid response and accurate reporting. Establishing a clear protocol for communicating such news is essential. Broadcasters should prepare for these instances by having reliable sources and contingency plans to deliver crucial information promptly while ensuring accuracy. A dedicated newsroom team can often help in this regard.
Managing Live Broadcasts and Technical Glitches
Live broadcasts come with inherent challenges such as technical glitches or unexpected interruptions. To mitigate these risks, broadcasters should ensure robust backup systems are in place, conduct thorough pre-event checks, and train the team on handling emergencies efficiently. Continual assessment of technology and spontaneous troubleshooting techniques will prepare broadcasters for unforeseen situations.
Compliance and Ethical Considerations
In the realm of sports broadcasting, adhering to compliance regulations and ethical guidelines is non-negotiable. Broadcasters must consider rights management, licensing agreements, and respect for players’ privacy. Maintaining integrity in reporting—especially in sensitive situations like injuries—can also protect a broadcaster’s reputation. Legal consultation should be sought for complex compliance issues to navigate these intricacies gracefully.
The Future of Sports Broadcasting
As technology continues to advance, the future of sports broadcasting looks exceedingly promising. Emerging trends are changing consumption patterns and audience expectations.
Emerging Technologies and Trends
Innovations such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are increasingly being utilized for data analysis, refining audience targeting, and enhancing the viewer experience. AI can also automate various production tasks, reducing human error and streamlining broadcasts. Moreover, machine learning algorithms are being used to predict viewer preferences and suggest personalized content, an invaluable tool for broadcasters seeking to engage their audiences more effectively.
Impact of Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are poised to revolutionize sports broadcasting experiences, creating immersive environments for audiences in ways previously unimaginable. VR can allow viewers to feel as though they are part of the game, while AR can enhance live broadcasts with additional visual information—stats, player insights, and interactive elements. Embracing these technologies can vastly enrich the broadcast experience and offer what traditional media cannot.
Predicting the Disruption of Traditional Broadcasting
As streaming services gain momentum and viewership shifts toward on-demand content, traditional broadcasting faces a significant disruption. Future-oriented broadcasters must adapt their strategies to align with audience trends, ensuring they provide compelling, flexible, and accessible content. This may include a greater focus on niche markets, flexible subscription models, and individualized content delivery.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is sports broadcasting?
Sports broadcasting involves the live coverage, analysis, and commentary of sporting events across various mediums, including television, radio, and online platforms.
How has sports broadcasting evolved?
Sports broadcasting has evolved from radio transmissions to television and, more recently, to internet live streaming, incorporating immersive technology and viewer interactivity.
What roles are involved in sports broadcasting?
Key roles include commentators, producers, technical crew, analysts, and graphic designers, all working together for seamless broadcasts.
What challenges do sports broadcasters face?
Common challenges include handling breaking news accurately, managing live broadcasts and technical issues, and adhering to compliance regulations.
What is the future of sports broadcasting?
The future involves leveraging emerging technologies like AI, VR, and AR, which are transforming viewer experiences and change traditional broadcasting methods.